Alkira Resources / Wiki / What is Cloud Networking?
What is Cloud Networking?
Cloud networking provides connectivity services between applications and workloads located in one or multiple public cloud environments. Such environments can be regions of a single public cloud provider, multiple public cloud providers (multi-cloud) or cloud edge computing environments located in either customer’s on-premises data centers or service provider’s points of presence. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications typically become an extension of the cloud network with regionally or centrally provisioned Internet exit points for access.
Cloud Networking Technology
Cloud networks can be delivered leveraging numerous technologies, including:
- Service Providers – Many service providers offer cloud interconnection services, such as the ability to connect customer MPLS networks to the cloud workloads. This is typically a premium service with additional service surcharge.
- Colocations – Colocation providers offer private cloud interconnection services to customers residing in the colocation facilities. Some colocation providers leverage software controls in the form of software-defined cloud interconnect (SDCI). Cloud connectivity is limited by the geographical presence of the colocations, which may not match the location of the cloud workloads themselves. Provisioning times and cost are typically high.
- Cloud On-ramps / Cloud Gateways – Software Defined WAN (SD-WAN) solution providers offer the ability to extend virtual wide area networks into the cloud through the use of cloud routers with automated integration into the cloud-native capabilities offered by the cloud providers themselves. This approach typically provides north-south access to the cloud with limited east-west networking capabilities.
- Do-it-Yourself Cloud Networking – Customers can leverage cloud-native capabilities of each individual public cloud provider to establish the desired connectivity. In this case, customers typically need to overcome restrictive cloud limits and disparate cloud architectures across the different cloud providers. This approach typically requires highly skilled personnel.
Cloud networking companies frequently integrate their offerings with cloud network security to provide the level of protection to the connected applications and workloads. Operational visibility and control are also typically part of the cloud network deployment.
Cloud Networking Benefits
- Scaling Cloud Network Workloads
A modern cloud network, fully integrated and provisioned in the cloud, inherently operates at cloud scale. These newer cloud network architectures are delivered on-demand only for when, where, and for as long as required. - Elastic Cloud Networking
Cloud workload costs are high and something every enterprise aims to control. By matching cloud network services capacity to demand in real time, a modern cloud network lowers costs for customers by allowing them to pay only for the network capacity they need to actually consume, rather than provisioning for workload peaks. - Security for Single and Multi-Cloud Networks
Securing the cloud network requires being able to seamlessly insert security and network services, such as multi-cloud network firewalls, directly into the solution. Since many enterprises have existing security infrastructure in place, cloud networking companies typically partner with top cloud firewall vendors to provide deep integration of cloud security into the network infrastructure. - IT Resource Optimization
Every cloud provider has their own unique constructs and limitations, requiring IT teams to learn every new cloud from the ground up before adding a new provider. Leading cloud network providers focus on abstracting that individual cloud provider complexity into their solution, allowing customers to treat every cloud the same. This greatly reduces time-to-service for enterprises looking to add new cloud providers to take advantage of application-specific innovations and cost offers. - Day-2 Cloud Networking Operations
Cloud network visibility and governance remains a major challenge for many enterprises, particularly in multi-cloud environments. A cloud network that can deliver end-to-end visibility and the insights required to optimize the network are essential elements of both a successful initial deployment and ongoing cloud network operations. In particular, the ability to discover and inventory the entire cloud environment allows for turning down costly unused workloads and closing cloud security gaps.
Emerging Cloud Networking Architectures
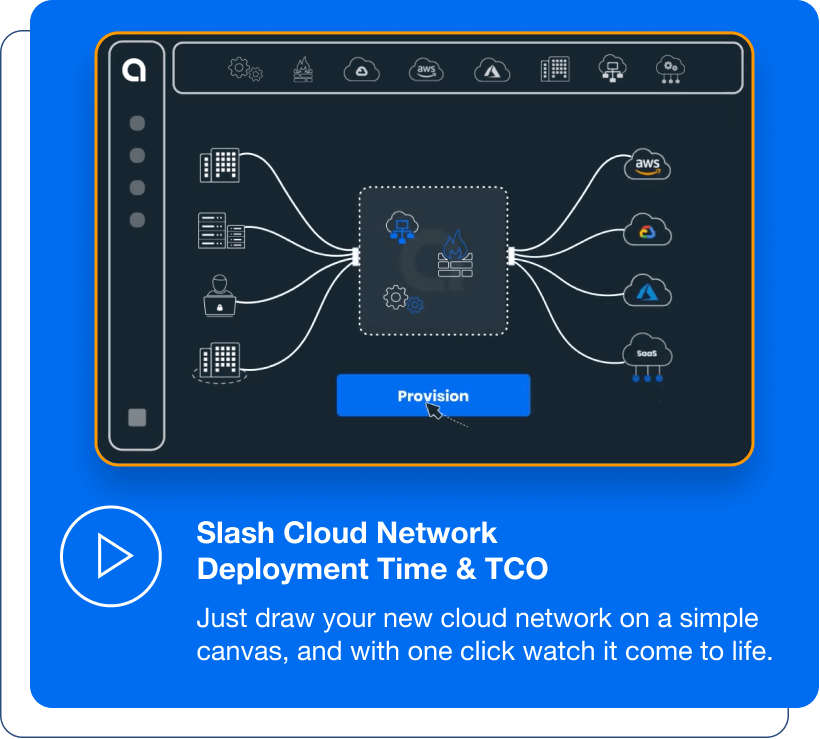
A new form of networking for the cloud has been seeing rapid growth with enterprises looking to fundamentally transform their multi-cloud adoption journey – Cloud Area Networking. This network, introduced by Alkira, combines all the benefits of traditional cloud networks but delivers the entirety of the solution within the cloud, offering unprecedented levels of agility and scale. By abstracting all of the underlying infrastructure complexity associated with legacy cloud networks, Alkira Cloud Area Networking allows customers to design and provision a global network entirely through a point-and-click UI, saving months of development when adding new cloud providers.