Alkira Resources / Wiki / How Does AWS Networking Work?
How Does AWS Networking Work?
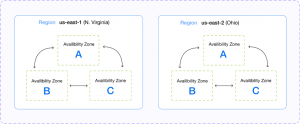
Amazon Web Services (AWS) interconnects regions, availability zones, and data centers via a purpose-built, highly available, and low-latency private global network.
- Regions are physical locations around the world that consist of clustered data centers called availability zones; Each region is physically isolated from and independent of other regions
- Availability Zone is one or more physical data centers; While a single availability zone can span multiple data centers, no two zones share a data center
What is VPC
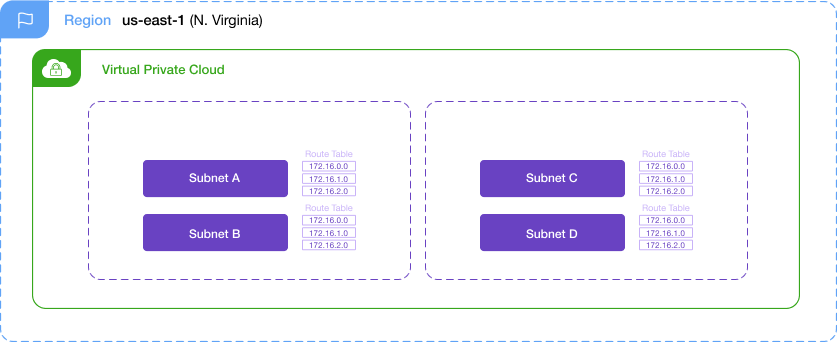
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) enables connectivity between your AWS cloud workloads, forming the foundation you need to run applications in the cloud. Each VPC is limited to an AWS region. At a foundational level, a VPC comprises of:
- Subnets created from the main VPC address space; Limited to a single availability zone
- Route Tables that influence traffic forwarding to external destinations
A VPC can reach the outside world through the following gateways:
- Virtual Private Gateway (VGW) enables the ability to have multiple VPCs, in the same region and account share a Direct Connect
- Direct Connect Gateway (DGW) extends Virtual Private Gateway capabilities by adding the ability to connect VPCs in one region to a Direct Connect in another region
- Internet Gateway (IGW) provides transport to the internet from your VPC; Horizontally scaled, redundant, and highly available
- Transit Gateway (TGW) connects multiple VPCs and on-premises networks through a central hub; supports inter-region peering
Note: Alkira is an official AWS Transit Gateway Connect partner. See press release.